What Is SEO? Search Engine Optimization Tips and Practices (2024)
Learn the basics of SEO and how Google ranks pages in its search results in this guide.
 February 14, 2024
February 14, 2024 12 minute reading
12 minute reading
It doesn’t matter if you’re starting an ecommerce store or offering a professional service online, you’ll come across SEO for marketing. And at first glance, it may seem like a can of worms you don’t want to open.
Thankfully, SEO is not as difficult as you might think. Primarily, the goal is to rank high on search engines like Google, ideally on page one.
This SEO guide will help you learn how to implement SEO to drive organic traffic to your website. After reading it, you'll understand why SEO is essential and how it can significantly boost your marketing efforts.
Find SEO services by SEO experts
What is SEO?
SEO means Search Engine Optimization. It’s the process of optimizing a website to get it seen when people search for products or services related to your business on Google, Bing, or other search engines. Getting more attention from search engine results makes your business more attractive to potential and existing customers.

To rank a site, SEO involves many strategies, including content quality and relevance, on-page and off-page optimization, keyword research, link building, and technical SEO. At the end of the day, it's all about answering searchers' questions and satisfying their needs.
The goal of SEO is to increase organic (non-paid) website traffic by improving your ranking and visibility in SERPs. This requires continuous effort and adapting to ever-changing algorithms.
How is SEO different from SEM and PPC?
SEO is more focused on improving your website’s visibility in organic search results. It’s a longer-term strategy that involves keyword research, creating high quality content, and ensuring a good user experience.
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) is a broad term that includes SEO, but refers to other marketing activities that improve your online presence, like paid search advertising, display ads, and shopping ads.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) is a paid marketing channel where you pay a fee each time one of your ads is clicked. Essentially, it's a way of buying visits to your site, rather than attempting to “earn” those visits organically. PPC can lead to faster results and are used for specific campaigns.
There are some overlaps between SEO, SEM, and PPC, but they have different strategies and uses.
In SEO, organic growth and long-term results are emphasized.
In SEM, organic growth and paid Google ads are combined for an aggressive approach.
In PPC, clicks on ads lead to faster results.
Why SEO is important
Your website content could be competing with millions of other businesses. So, when your content ranks high on Google, the more likely people will click on the website.
Ranking on page one significantly increases click-through rates. For instance, typically, on the first page of Google, the number one listed organic result averages a 39.8% click-through rate. The second position is 18.7%, and the third has a 10.2% click-through rate.
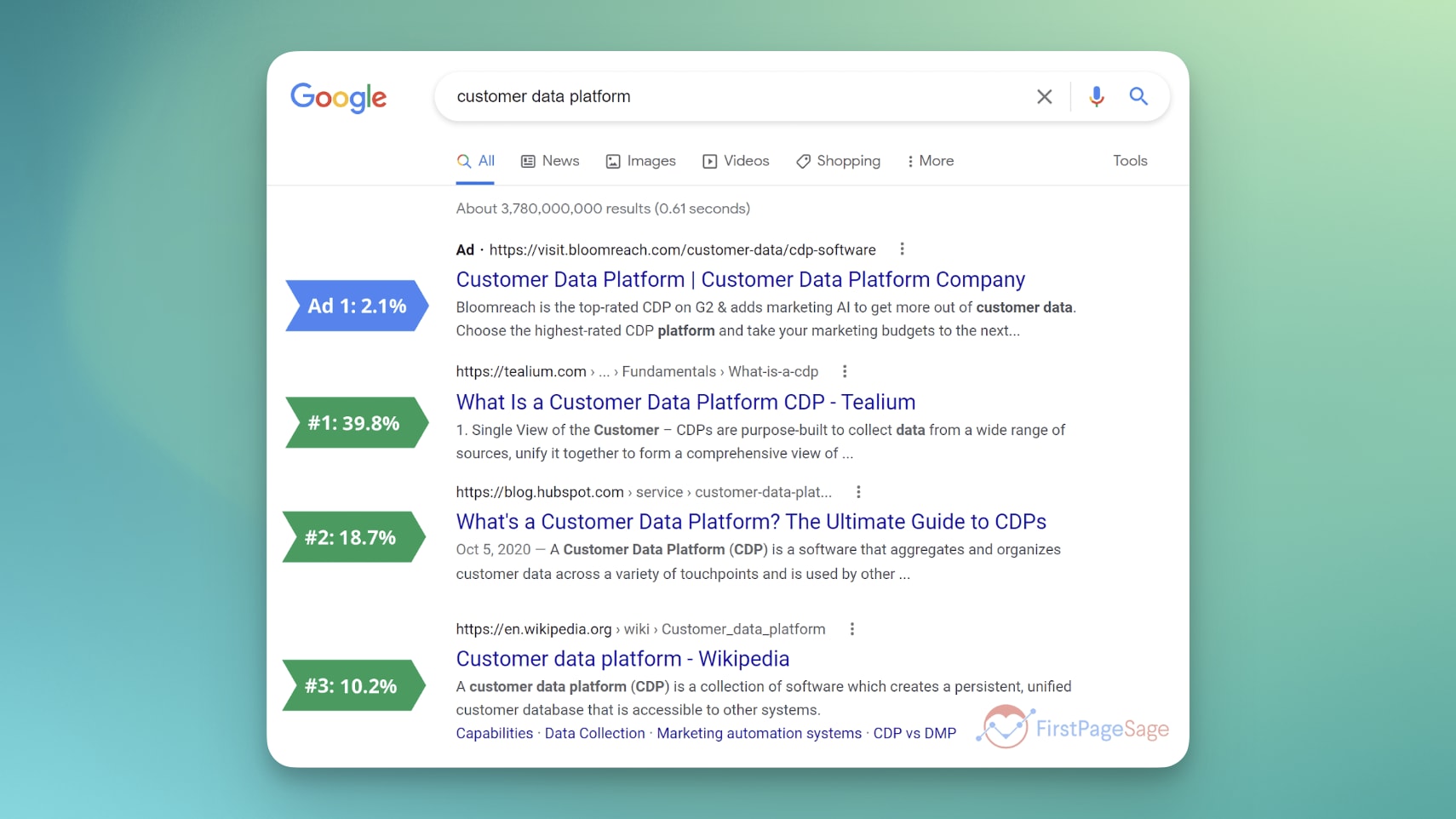
Source: FirstPage
Organic traffic is the optimum source of attracting customers to your website. Firstly, it's cost-effective, with no need for expensive paid ads. Secondly, it can result in high conversion rates because it generates highly qualified leads. Finally, as intent drives user searches, you can tailor content to address your ideal target audience.
How search engines work
A search engine is an automated, highly-developed software program that helps people quickly find the information they want by typing in phrases or keywords. Search engines use predefined algorithms that can rapidly produce the best results.
Search engines use robots to scan the Internet continuously, crawling and indexing pages. For every user search, the algorithm checks the titles of indexed web pages, including keywords and content. It then produces a list of relevant sites in ranking order, with the perceived best value websites on page one.
The three stages of a Google search:
Crawling: Google automated robots (Googlebot) crawl the internet 24/7, using an algorithmic process to identify content, images, and videos from web pages, which are then downloaded to the database. The robots follow link trails on your site, which is why a site map can be helpful. Google crawlers need full access to a website, which can be prohibited by network issues, robots.txt directives blocking Googlebot, or problems with the server hosting the site.
Indexing: A site is invisible until it is indexed. Google analyzes a web page's content, images, and video files, considering elements like content, titles, headings, alt tags, meta tags, etc. Google determines if a page is canonical (most likely shown in search results) or a duplicate. It then stores the information in the Google Index. There's no guarantee that Google will index your site. It may have a poor design or metadata or low-quality content. Google wants to return the highest quality content to its users.
Presenting search results: When a user inputs a keyword or phrase on Google, the search engine returns relevant websites. Hundreds of factors determine relevancy, such as users' language, locations, and what device they're using.
Google and SEO
Most companies target their SEO optimization for Google guidelines as it is the most dominant search engine. Still, optimizing for Google also helps businesses rank with other popular search engines like Yahoo and Bing.
Google uses several hundred factors to determine your PageRank and generate search results. Google uses over 200, so if you optimize your website for the essential factors, Google robots will crawl and index your site. If your website is not indexed, it will not feature in search results.
Google also provides a ton of free tools to help you rank, like Google Analytics and Google Search Console. These tools show all the juicy metrics (like bounce rate and CTR), as well as all the search terms your business ranks for, so you can make smarter decisions.
What Google wants
Google wants to return the best quality pages with relevant content that help its users.
Google assesses three sections of a website:
The main content: Such as written content, images, and videos
Supplementary content: Contributing to a positive user experience but not directly influencing the page purpose
Advertisements: A business can make money from monetizing its website, but sponsored content must be apparent to the user
Site navigation must be well maintained and user-friendly with working links, optimized images, and site information that helps visitors learn about your company.
The reputation of your website may influence search results. Regularly check review sites like TrustPilot and Yelp and integrate improvements where needed.
The high-quality main content on your site is essential for a good rating, and supplementary content supports page quality. When writing for SEO, follow the "EEAT" principles:
Expertise
Experience
Authoritativeness
Trustworthiness
Create an informative site that positions you as a trustworthy expert and authority in your industry.
Sites with a lack of, or poor quality, content that lacks the "EEAT" principles are considered low-quality. In addition, other factors are a negative reputation, poor page design, broken links, keyword stuffing, lack of information about the company, and out-of-date pages.

Source: Search Quality Rater Guidelines
Unsurprisingly, the quality and quantity of your main content are the top factors for page quality. In addition, a strong foundation of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness are equally important. Still, these components won't matter if your business has a poor reputation.
How Google makes money
Google's primary revenue source is advertising, where businesses pay to have their ads appear in Google's search results and on websites in the Google Display Network. Another significant source of income is YouTube, through ads displayed in videos. According to the latest earnings report by Alphabet, Google’s parent company, total worldwide advertising revenue for Q3 2023 was $76.7 billion, up 11% year over year.
Google Cloud services, offering cloud computing and storage, contribute to their revenue through subscription-based models. Sales from the Google Play Store, including app and in-app purchases, also add to Google's earnings. Additionally, Google generates income from selling its own hardware products, like Pixel smartphones and Google Nest devices.
Types of SEO
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is about optimizing your website and server in a way that helps the search engines to more effectively crawl and index your website, which will help improve the site's organic ranking.
On-page SEO
On-page is everything you do on-site to optimize website pages to rank higher in the search engines to get relevant traffic. On-page SEO includes page content, HTML source code, Meta tags, adding images with "alt" descriptions, FAQ schema, video SEO, and adding internal and external links to pages.
Off-page SEO
Off-page (often called off-site SEO) is the external action taken to improve your search engine ranking. For instance, it may include guest posts, social media marketing, podcasts, brand mentions (linked and unlinked) etc. The aim is to create quality, trusted backlinks to your site to build domain authority (DA).
Local SEO
This targets local search specifically, optimizing a business's presence for local searches, such as "near me" search queries, by optimizing for local listings and maps. It can also help you show up on Google Maps, which can help you reach more searchers.
A Google Business listing is one of the most critical steps in local SEO. You must include accurate and up-to-date information such as the business name, address, phone number, business hours, and categories, as well as manage customer reviews and post updates.
The anatomy of search results
When you enter a keyword or phrase into a search engine, it returns SERPs (search engine results page). Google is the most popular search engine, with more than 80% of the market share. Other search engines include Bing, Yahoo, and Yelp.

The average search results include:
Paid search, where companies have paid to at the top of page one
Organic results determined by the Google algorithm
Featured snippets
Additionally, some queries will return search results pages containing the following:
Local Pack of Google Business Profile listings
Video Results
Images
Knowledge Graph - containing information about a certain query (information gathered from a variety of authoritative sources)
SERPs are important for SEO because they determine how your site appears on Google's first page, and you can help it influence your chosen page keywords.
For instance, if your keyword is "best podcast microphone" and a search returns ten paid adverts, your site sits beneath them. You research a different keyword, such as "top 5 best podcast microphones", and there are only two paid ads, meaning your site is in the third position on the first page.
For a highly competitive keyword, paid searches may also appear at the bottom of the first page, making it increasingly challenging for organic results to get onto page one.
What a perfectly SEO optimized page looks like
SEO needn't be complex. The principles are simple, but to formulate an SEO strategy, knowing the anatomy of a perfectly optimized page helps create a streamlined SEO plan and improve your content marketing efforts.
Title Tag
Having a keyword in the page title tag can act as an SEO signal. Title tags beginning with a keyword outperform title tags with the keyword at the end.
H1 Heading
When the keyword is in the H1 tag, it's a "second title tag" that Google uses as a signal for secondary relevance.
Mobile-Optimized
Over 50% of Google searches are from a mobile device. Subsequently, Google now penalizes websites not optimized for mobile users.
Content Length
Longer content outperforms short-form content, primarily because longer word content can cover a subject in more depth, providing more user value. A recent industry study on ranking factors revealed that the optimum content length is around 1400 words.
Internal Links
Internal links are an essential component of SEO. For instance, if you have a page starting to rank, pointing to more internal links of relevance creates a ranking signal. Note that internal links with more authority are more effective than a low-ranking page.
Image Optimization
Optimize images with relevant captions, alt text, file names, titles, and descriptions because it helps to send essential relevancy signals to the search engines.
Page Experience
Google considers page experience as a ranking factor and uses a subset of factors called core web vitals to determine a web page's overall experience.
Where to learn SEO
The internet is ripe with places to learn about SEO. But here are the top places to find lessons taught by experts in field:
Semrush Academy: Semrush is a popular SEO tool and their academy offers free courses and exams to test your knowledge. It's great for both beginners and advanced users.
Moz: Moz is a highly respected name in the SEO community. They offer a variety of resources, including blogs, guides, and Moz Academy with courses for all levels.
Yoast SEO Academy: Known for their WordPress SEO plugin, Yoast offers courses that cover a wide range of SEO topics, from basics to technical SEO.
HubSpot Academy: HubSpot offers free courses on digital marketing, including SEO. Their courses are comprehensive and include certifications.
The role of SEO in digital marketing
SEO is a fundamental aspect of your digital marketing strategy. It's crucial in helping search engines crawl your website for indexing into their catalog of content. There are some ways to rank fast in SEO, but your SEO efforts should be focused on the longer term.
Allocating an SEO expert to underpin your marketing plan can be an efficient way to impact the bottom line. These professionals know how the search engine algorithms work and can provide the best SEO tips and practices for a small business to rank in relevant results.
Fiverr offers a large marketplace of freelance SEO experts. You can use Fiverr’s chat system to talk to sellers before you hire them. Plus, use a single dashboard to manage people, places, and project files — all for no monthly charge.
Sounds good? Sign up for a free Fiverr account today to start.
SEO FAQ
What are the four types of SEO?
On-page SEO
Off-page SEO
Technical SEO
Local SEO
What does SEO stand for in business?
SEO stands for Search Engine Optimization in business. It's a digital marketing strategy focused on increasing your website's visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs), mostly through organic (non-paid) methods, to drive more traffic and increase business revenue.
What is an example of SEO?
An example of SEO is a blog optimizing its content for certain keywords to rank higher on Google. This could involve using specific, relevant keywords in the title, meta description, and body of the blog post, making your site mobile-friendly, and gaining backlinks from reputable websites.
How does SEO work?
The goal of SEO is to make your site more search engine-friendly by optimizing its content and structure. When search engines crawl and index web content, they rank it based on things like keyword relevance, site usability, page speed, and backlinks. A website's ranking higher in search engine results makes it more likely for people to find it and come back.