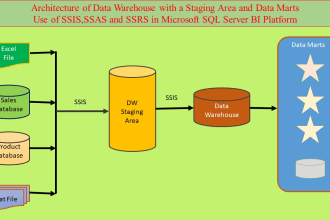
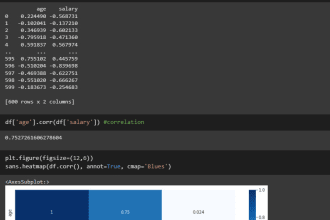
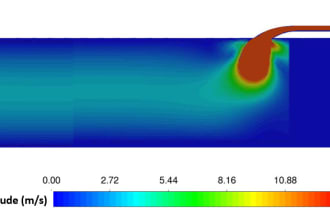
Browse categories
Data Engineering
Work with an engineer to build and maintain your data resources.
|2,000+ Results
Sort by:

Level 2
I will perform k means clustering, hierarchical clustering and dbscan
From $20Offers video consultations
Data Engineering FAQs
What is data engineering?
Data engineering is the handling and processing of data between the stages of data creation/capture and data science/analysis. The data pipeline of an organization works through the stages of ingestion, processing, storage, and access, and data engineering uses technical approaches and techniques to improve internal processes and communication. Data engineers ensure that raw data are made accessible for the practical use of data scientists and other groups. Data engineering is often categorized as a subset of data science.
What are the key fields and processes in data engineering?
Data engineering includes planning, designing, building, testing, and maintaining data systems, and there are key fields that fall under the term. Data flow is the organization and management of raw input data from different sources. Data normalization and modeling involve the transformation and conformity of data to data models. Data cleaning ensures that all data are clean, correct, and without duplicates or incomplete or corrupted files. Data accessibility is the responsibility of data engineers to ensure that data are easily accessible from the database or repository for the end user.
How can data engineering services benefit my business?
More and more business today are data-driven. They increase the role of data in their operations, which makes data engineering an essential service. With the rise in the importance of data science and analytics, data engineers are needed to facilitate data flows and prevent costly bottlenecks. Data scientists and analysts frequently lose valuable time to dataset activities that could be more efficiently performed by data engineers, so establishing and defining this role is a sensible move for an organization.
What are the most important data engineer skills?
There are a number of skills that data engineers need to be equipped with to meet the requirements of the role. Data engineers need experience with backend technologies like SQL and NoSQL, as well as programming languages like Python, Java, and Scala that can be useful for dealing with large data sets. Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud platform that data engineers use to design automated data flows and Apache Hadoop is a useful set of tools for supporting data integration. Kafka is a software platform for building real-time streaming apps. It is useful for data engineers to have skills for all of these tools. In addition to these technical skills, data engineers also need essential soft skills, such as clear verbal communication and writing skills.
Which tools and frameworks do data engineers use?
Data engineers need to connect with databases and backend frameworks so they can collect, store, and transfer large sets of data. Databases used for storage include SQL, NoSQL, and PostgreSQL, and they may be provided by vendors like Oracle, Azure, or Amazon. This technology allows data engineers to organize and manage different types of data quickly and efficiently. Data engineers also need to be able to use a wide range of applications and frameworks, including Python, Spark, Hadoop, and Kafka, for tasks ranging from coding ETL (extract, transform, load) frameworks or API interactions to scaling and processing of multiple data sets across different devices. If you need your data engineer to effectively capture, store, manage, and distribute of data, it's important for them to be proficient with these tools.
How is a data engineer different to a data scientist?
While data scientists are concerned with the analysis and interpretation of data, data engineers lay the groundwork for them to receive data from various locations. The work of a data scientist involves identifying trends and relations in business and market operations research through the application of machine techniques and methods to data. Data engineers make this possible by providing the high-performance infrastructure that enables the collection of insights from raw data. Data scientists are dependent on data engineers, although the two roles share some tasks and similarities.